What is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction?
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, or PTTD, is commonly referred to as adult-acquired progressive flatfoot. Chronic musculoskeletal dysfunction affects the tendon, muscle, joint, and spine and is progressive and debilitating. Though the name suggests only the tendon is dysfunctional, it affects more than that specific tendon.

If the posterior tibial tendon is not functioning adequately, the ligaments surrounding it are affected, whereby the foot arch begins to flatten and decreases foot, ankle, and lower limb function. This condition only worsens over time, significantly increasing the chances of injury.
The posterior tibial tendon is vital in maintaining the arch of your foot, which is important for your biomechanical gait health and avoiding injury.
Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
The common symptoms of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction include swelling, pain in the area, flattening of the arch, and the inward roll of the ankle. Some patients with PTTD also may experience their feet feeling ‘flatter’ after hiking, walking, or running. These symptoms will only worsen over time; a lack of ankle stability increases the chances of falling and subsequent injuries. If left untreated, PTTD can have a deteriorating effect on your feet.
There are several different causes and risk factors for PTTD. Tendons usually degrade over time, breaking down with age, and older patients are more likely to experience this dysfunction. Obese patients who place more strain on the tendons in their feet are also at higher risk. Prior injuries can also increase the chances of PTTD, as the foot overcompensates for a weak ankle, foot, or joint.
As mentioned before, PTTD is not limited to the posterior tibial tendon. Several studies have attempted to recreate the condition on cadavers. By manipulating the ligaments surrounding the tendon, they were able to recreate the conditions of pes planus with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
This suggests that a treatment plan for PTTD needs to do more than simply think about the tendons; it requires a holistic approach to the whole foot to promote healing and slow down deterioration.

PTTD in Athletes
Overuse in the muscles of the foot often causes posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Athletes at risk are regular runners, volleyball players, and tennis players. In these cases, it can develop slowly but also arise abruptly due to an acute trauma like a nasty fall. In both these cases, it is vital to treat PTTD early before the symptoms worsen.
Studies have found that the earlier your PTTD is treated by a sports podiatry clinic, the faster your recovery is. This may seem obvious, and for athletes, this is vital.
To stay in your top-performing condition, you must treat your PTTD. Insisting on participating in sports with your injury will only worsen the PTTD and potentially put you out of commission entirely. If you are resting your foot to recover, returning too early can undo all the healing your foot has done and potentially re-injure the foot. Like many sports-related injuries, it’s better to play it safe than play too soon.
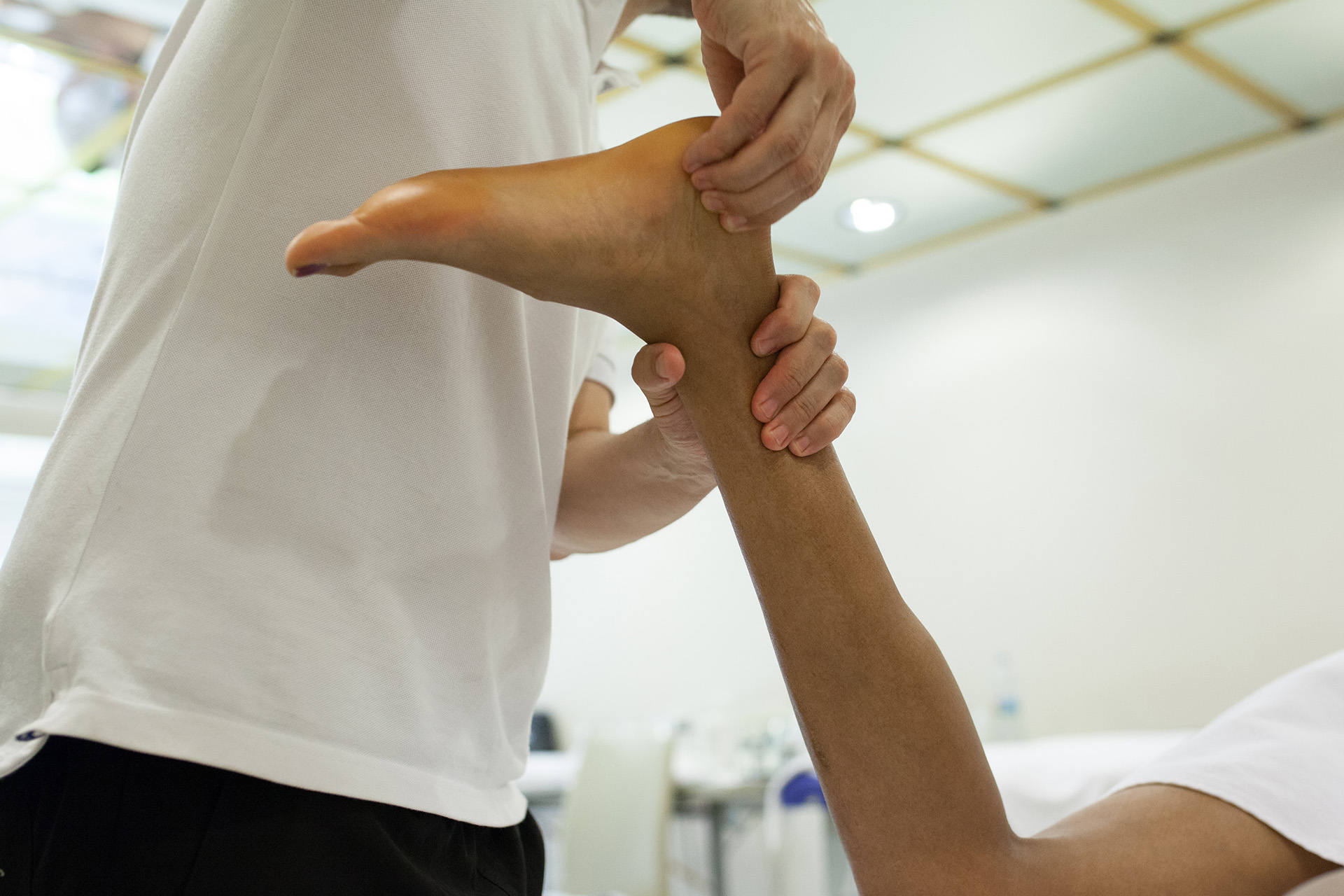
How is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Diagnosed?
Your podiatrist will examine your foot and look for noticeable swelling surrounding your posterior tibial tendon across your ankle and foot. They will also test your range of motion, manually moving your foot across different axes, to see whether it causes pain or discomfort. Pain moving the foot through its normal range of motion is a potential symptom of PTTD.
Depending on the severity of your PTTD, it could be either easier or more difficult for your podiatrist to diagnose the condition.
For example, patients with later posterior tibial tendon dysfunction stages tend to have ankles that are misaligned with the ground, turning inward. This is because, without the support of the arch, the foot curves inwards, and the ankle responds accordingly to counterbalance.
For this same reason, your podiatrist may have you attempt single-leg heel rises to see if one foot can support your body’s weight. Healthy patients should be able to do 8 to 10 rises, whereas patients with PTTD may not be able to do even a single heel raise.
Following these tests, your doctor or podiatrist may need to conduct further tests, like X-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds, or CT scans, to ensure your condition. These tests will allow your doctor to see the inner workings of your foot and give them the knowledge they need to recognize and diagnose your condition.

Conservative Treatments and Noninvasive Interventions
The effective treatment of musculoskeletal (MSK) conditions like posterior tibial tendon dysfunction involves a spectrum of interventions, including early diagnosis and assessment to restore optimal function.
Early management with conservative treatment options for PTTD without resorting to surgery or invasive interventions can help with the foot’s function and pain. The non-operative podiatric interventions include the following:
- Foot Mobility Assessment To best understand how far along your PTTD is, your podiatrist may conduct a foot mobility assessment to see where your foot, within its range of motion, experiences pain or discomfort. This assessment is essential in evaluating what kind of treatment, such as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction exercises, may suit you best and how severe it should be.
- Footwear In the early stages of PTTD, footwear can significantly help prevent further deterioration. Finding a shoe with a rigid midfoot and rubber sole is essential to best control the foot’s motion during walking. Before purchasing a new pair of shoes for your condition, you should check with your podiatrist to assess the best walking shoes for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
- Dry Needling The tibialis posterior muscle is subcutaneously located below the skin, as it can’t be directly palpated. Using this treatment method, a podiatrist targets your myofascial trigger points to release tight muscles and the connective fascia tissue to restore proper function.
- Braces One major outcome of PTTD is a weak ankle that cannot accommodate the lack of stability in the foot. An ankle brace can offer relief for this specific issue. Most posterior tibial tendon dysfunction braces allow for custom fitting to ensure your foot gets adequate support for your particular needs.
- Offloading Boots Offloading boots are large pieces of footwear, designed to minimize foot movement and the ankle joint and reduce the pressure placed on the foot during normal activity. Offloading boots can help ensure the patient’s foot gets adequate rest so the afflicted tendon and ligaments recover.
- Orthotic Therapy & Orthoses Your podiatrist can also provide custom-made orthoses to place within your shoe to provide ample flat foot support to support your arch. These orthotic devices will be tailored to your specific condition and designed for your foot.
- Shockwave Therapy For more severe PTTD cases, a few sessions of shockwave therapy can noninvasively repair tendons with acoustic waves to stimulate tissue growth for the lower limb tendinopathy.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, it is best to get an assessment at our sports injury clinic in Singapore to see if conservative treatments can help to reduce pain and improve the foot’s function. Make an appointment with our podiatry team today for a consultation.
FAQs about Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Is surgery necessary to treat my PTTD?
No, surgery is not essential to treat PTTD unless the situation is extremely severe. In many cases, noninvasive treatment can relieve patients with PTTD and give the foot the chance to rest and heal.
How do I know if I have PTTD?
There are several symptoms of PTTD, including soreness and pain in the foot area, an ankle turning inwards, or the arch of the foot flattening. The best way to know for sure, and to receive proper treatment, is to go to your podiatrist, who will conduct a proper assessment.
What can I do to fix my PTTD?
Several noninvasive options are available, like orthoses, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction brace, offloading boots, or physical therapy strengthening exercise programme. Outside of that, there are lifestyle changes you can make: losing weight can ease the pressure on your feet by reducing the load they carry, and wearing proper footwear with ample support can also relieve pain.
Will I have PTTD forever?
Some patients may need to wear insoles for the rest of their lives to avoid pain. Some patients may catch PTTD early and can prevent degradation by changing shoes. Most importantly, receiving proper medical care from a professional is essential. The sooner you catch PTTD, the lower your chances of subsequent injury.