Sports injuries can affect the way the body develops in children, impacting their bone growth and tissue maturity. Minor injuries, such as strains and sprains, often heal on their own. Sometimes these childhood injuries can become niggling issues as a growing body readjusts to misalignments, leading to a lifetime of adjustments and future sports injuries in children and adolescents, as well as in adulthood.
As the musculoskeletal system matures, children’s bones are more prone to injury because they are more susceptible to acute, traumatic impacts while they harden, leading to buckling or bowing. Similarly, bone growth occurs faster than that of supporting soft tissues and ligaments, which can be easily injured when pushing beyond the body’s ability to support.
The majority of injuries that occur during childhood from sports often appear normal in later life. Usually, injuries will fully recover with care, without invasive surgical procedures, and only require preventive measures and conservative treatments to safeguard against long-term complications.
For injuries such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears or Sever’s disease, paediatric sports medicine can help rehabilitate acute or chronic conditions so your child can enjoy sports without pain. Sports podiatry for children at The Foot Practice uses pioneering technologies, such as 3D Gait Analysis, to break down, analyse, and improve complex human movements, enhancing optimal sports performance in young athletes.

Musculoskeletal Growth in Childhood
Insights into the musculoskeletal peculiarities as the body grows are integral to understanding how to prevent and rehabilitate kids’ sports injuries. Genetics plays a large role in determining roughly 60 to 80 percent of your size and the strength of your bones; environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle choices, make up the rest.
During birth, bone density remains the same for both boys and girls, but during puberty, bone mass in males increases more because of a longer period of rapid growth, resulting in larger bones in men. (Read more about adolescent biomechanics in our article about the major physical changes in male and female growth changes that increase the risks of injury and running mechanics as our children grow into their adolescent years.)
During growth periods in childhood, bones and surrounding tissues become more susceptible to injury. Areas in the bone, known as growth plates, begin to lengthen while the surrounding tendons, joints, tissues, and ligaments do not develop at the same time. Tightness and inflexibility begin to develop as bone development outpaces growth in the surrounding areas supporting it.
Injuries in kids’ sports can vary in frequency depending on the movements required for the activity. Children who participate in track and field, for example, are more prone to suffer injuries in the hips, legs, ankles, and feet. In other sports for kids, such as gymnastics or dance, trauma often occurs in the spine as a lot of back extensions are used in the sports, resulting in damage to developing areas of growth.
Injuries can be either acute, such as in fractures and sprains, or gradual due to repetitive microtrauma, such as stress fractures, osteochondritis dissecans (OCD), apophysitis, or tendinopathies. In the majority of cases, sports injuries can be prevented by taking a few basic precautions, such as dynamic stretching, wearing appropriate clothing, and early detection of potential injuries.

Soft Tissue Sports Injuries in Children
A number of risk factors contribute to paediatric musculoskeletal injuries. Soft tissue injuries can involve ligaments, tendons, and muscles and often result from overuse, trauma, sprains, or strains. More specifically:
- Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments connecting the bones of the foot are injured due to excessive stretching or tearing. Ankle sprains in sports can occur when an athlete lands on the foot in the wrong way, causing the ankle to roll and place it out of its normal position.
- Contusions, also known as bruises, occur from impact and are common in kids’ sports. When a contusion occurs, small blood vessels under the skin are torn, resulting in a black-and-blue appearance in the area.
- Lacerations occur when your skin is cut or torn, which can happen during sports, falls and collisions during play.
- Strains result in muscles and tendons which are partially or severely stretched or torn. Strains usually cause pain, inflammation, and swelling, with restricted movement in the affected area.
If your child suffers an acute soft-tissue injury, the best remedy is a little PEACE and LOVE protocol to address the inflammatory healing response and pain immediately. If the condition lasts more than a few days, a subsequent podiatric assessment may be needed to support injury rehabilitation.
Acute, Traumatic Sports-Related Injuries
Acute injuries in children can happen at any given time while participating in sports due to a sudden impact on an area of the body, resulting in sprains, strains, breaks, and dislocations. Injuries can occur from a fall, a sudden turf toe injury while kicking the football, or repetitive use while running in improperly fitting footwear that leads to an acute event.
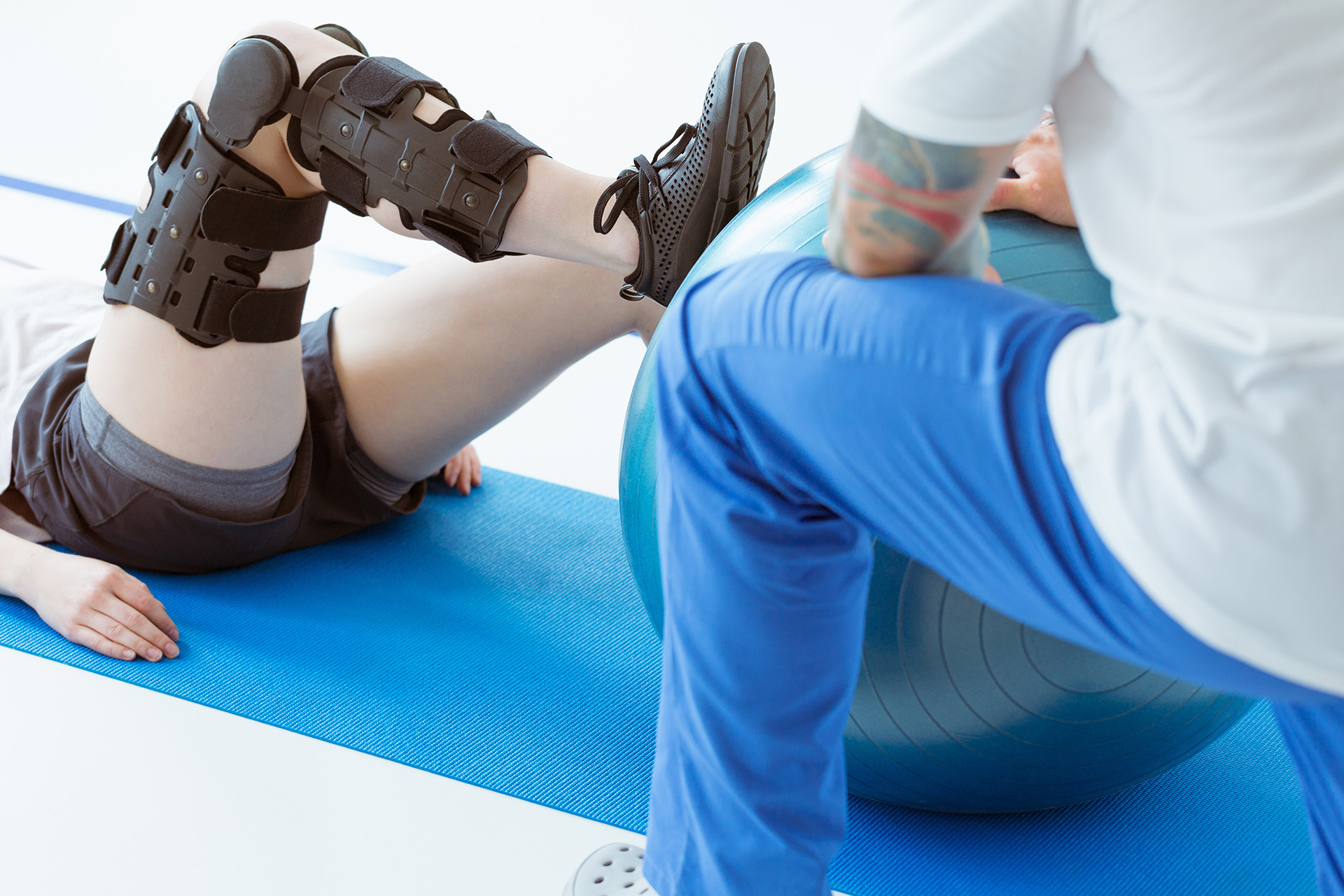
Acute injuries in children usually impact a specific area of the body, which receives the impact from the source of the trauma. Often, a proper podiatric assessment and foot care treatment plan can address the condition, restoring optimal function and helping the child return to sports as quickly as possible. Some common adolescent acute injuries we see at The Foot Practice include:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries manifest as over-stretching, or complete or partial tears of the ACL in the knee connecting the femur to the tibia. Those with ACL injuries often require significant time off from sports, as movement is often severely restricted in the knee and leg.
- Patella dislocation occurs when the patella, which helps the knee to bend by moving vertically along the trochlear groove, pops out of place, usually tearing the tendons and ligaments supporting it.
- Meniscal injuries can occur when the meniscus, which serves as a cushion for impact, is forced to twist or turn. Symptoms show as pain, swelling, and weakness in the knee.
- Turf toe is a sprain of the ligament in the big toe due to hyperextension from being forcibly bent upwards. This is a common sports injury in which the toe is forced into a bent position, often in runners and football players, and can be exacerbated by tight, narrow footwear.
Early diagnosis and treatment of injuries is critical in returning young athletes to their sport safely and quickly. Any injury that involves obvious swelling, deformity, and/or loss of normal function (e.g., movement or strength) should be seen by a physician immediately.
Common Overuse Injuries in Children
Overuse injuries appear when repetitive stress or microtrauma occurs on a joint or muscle, leading to pain, discomfort, and inhibited motion in the area. When engaging in adolescent and kids’ sports and athletic activities, risk factors such as sport specialisation at a young age, imbalance of strength or joint range of motion, anatomic malalignment, improper footwear, and intense, repetitive kids’ sports training regimens can predispose children to overuse injuries.
Common paediatric sports injuries include:
- Osgood-Schlatter disease, which affects children during growth spurts, is more common among those who participate in sports that require running and jumping. Ailments from this disease arise from greater impact on the upper portion of the shin bone and the knee, leading to inflammation.
- Osteochondritis dissecans is a joint injury that often occurs in children due to high-impact sports, such as running, jumping, or handsprings, or from repeated pressure on certain joints. This causes the bone under the joint to die due to a lack of blood flow, potentially breaking off and inhibiting motion in the area.
- Sever’s disease, also known as calcaneal apophysitis, often results during maturity when engaging in sports. During this period, bone growth occurs faster than tendon growth, causing the Achilles tendon to pull the heel back. This results in repetitive stress, which manifests in the body as symptoms of heel pain due to inflammation.
- Shin splints cause pain and discomfort along the front of the tibia, the large bone in the leg connecting the knee to the ankle. Shin splints result from increased workload, often due to elevated kids’ sports training routines, when excess pressure is exerted on tendons, muscles, and bones in the area.
- Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (SLJ) presents with pain or swelling at the cartilage just below the knee cap (patella), where the growth plate is located. SLJ usually resolves without long-term issues after children finish growing during their teenage years.
- Spondylolysis is a stress fracture found in 5 percent of adults affecting the pars interarticularis vertebrae, a thin bone section connecting two vertebrae in your lower back.
- Stress fractures are small cracks in your bone that result from repeated stress or trauma occurring over a long period of time. Although stress fractures can happen anywhere in the body, they occur much more frequently in the lower extremities due to running and jumping in sports for kids.
Niggling injuries in children that go untreated or misdiagnosed can turn into chronic problems that require a much longer time away from the sport to allow the injury to heal properly.
Podiatric Treatments for Paediatric Sports Injuries
Paediatric foot care for sports allows for early intervention and treatment of dysfunctions or acute injuries in a child’s growing foot. When it comes to paediatric sports medicine in Singapore, The Foot Practice’s paediatric podiatrist addresses and corrects abnormalities and musculoskeletal injuries so that your child can continue to participate in sports without complications, pain-free and with full mobility.
Non-surgical methods include performing specific stretches, participating in strengthening and range-of-motion exercises for physical therapy, wearing specialised braces for the foot or ankle, wearing orthotic insoles, or altering their current physical activities to accommodate a specific musculoskeletal disorder. Depending on your child’s condition, there are many conservative, noninvasive options for treating your child’s foot condition, which may include complementary treatment protocols:

Footwear Assessment and Children’s Shoe Advice
Athletic shoes have come a long way since we were kids. The scientific engineering behind children’s footwear has advanced to improve comfort and boost performance, while remaining “on-point” and fashionable. Unfortunately, the most socially shareable shoes may not be the best for biomechanical movements.
The wrong footwear choice is often the direct cause of your child’s sports injury. Our podiatrists provide Footwear Assessments for your child to address any mechanical overload from improperly fitting shoes that impede injury recovery.
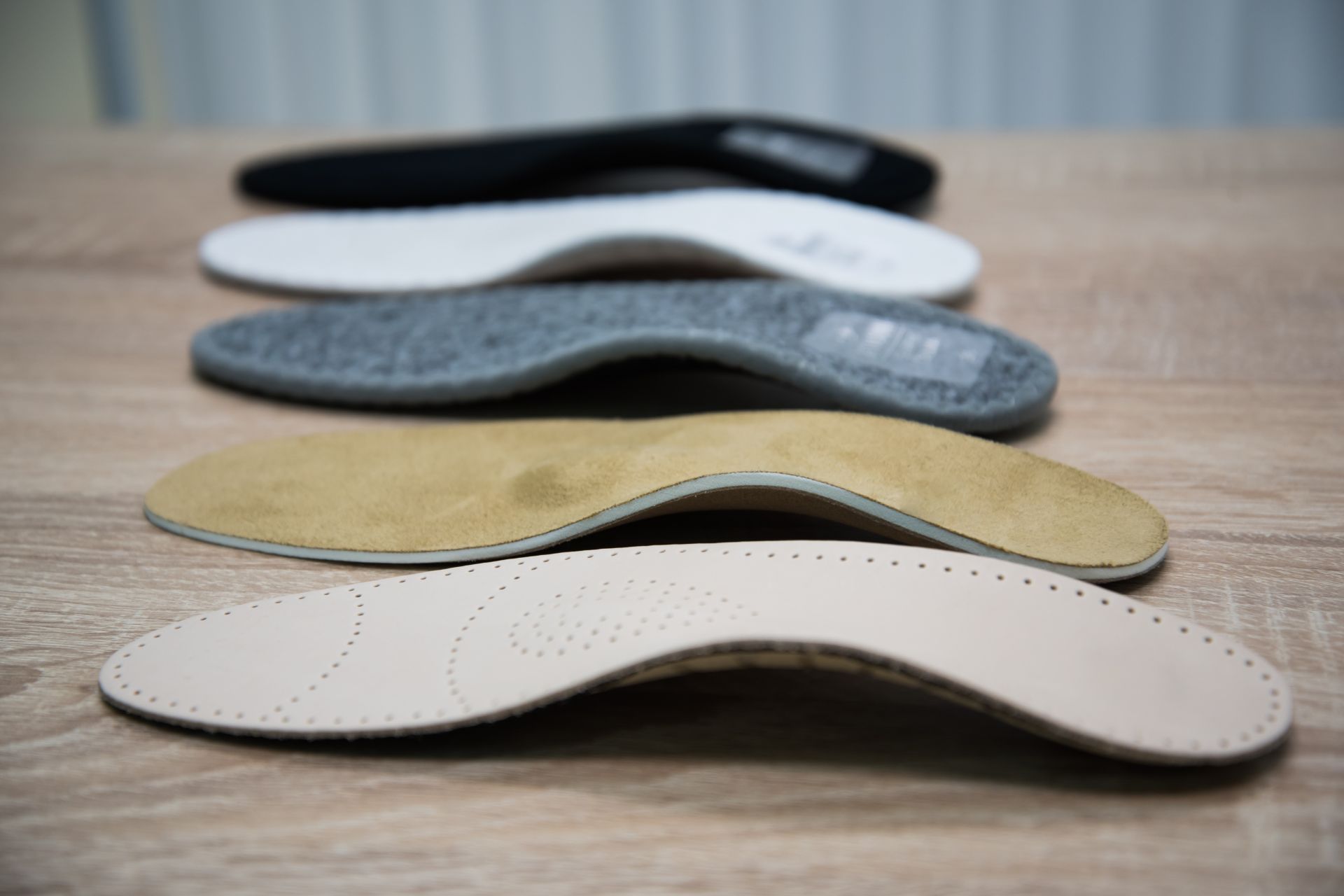
Paediatric Orthotic Therapy and Customised Insoles to Address Foot Dysfunctions
Orthotic therapy and custom insoles can address some of the most common musculoskeletal lower limb disorders in children and adolescents, such as metatarsus adductus, flexible flatfoot, clubfoot, and other functional disabilities. We see a lot of young patients who require treatment after a sports injury or to address niggling pain that prevents them from fully participating at optimal sports performance levels.
Oftentimes, the best treatment for children’s foot conditions is custom-made orthoses, accompanied by other therapeutic recommendations. The combined clinical therapies are extremely effective in treating children’s foot conditions, including plantar fasciosis, high arches or flat feet, and overuse injuries such as Achilles tendinopathy.
Many ailments that arise in the body, such as poor posture, muscle imbalance, and alignment, are due to abnormalities in lower leg and foot mechanics that can be corrected with custom orthoses or prefabricated devices, thereby decreasing pressure on the hips, spine, and shoulders.
3D Gait Analysis for Young Athletes
Biomechanical gait analysis is optimised with pioneering 3D technology to improve athletic performance and diagnose misalignments. The Foot Practice’s pioneering 3D Gait Analysis can be used for both high-performing young athletes looking to achieve marginal gains and for athletes with deformities that impede normal walking gait. Results from 3D Gait Analysis can then be incorporated into training and recovery plans, optimising and enhancing results for young athletes.
Foot Mobilisation Therapy
Foot Mobilisation Therapy is a treatment modality that helps restore joint movement by assisting the foot and its joints through their natural range of motion, helping them overcome any restrictions that may be inhibiting optimal function and range of motion.
The therapy helps improve synovial fluid production, which is important for the healthy well-being of cartilage in the joints, while lessening pain by stimulating joint receptors in the foot. In many cases, the treatment is accompanied by an additional rehabilitation regimen aimed at further guiding the foot toward full function by building strength and improving the range of motion.
Muscle Strengthening and Neuromuscular Rehabilitation
Muscle strengthening in the foot and surrounding areas is important for preventing sports injuries, treating ailments such as shin splints, plantar fasciitis, and sprains, and enhancing the ability to perform in sports by improving balance and stability.
Muscle-strengthening exercises may be prescribed alongside other treatment options to help build strength in the targeted and surrounding areas. Combined with neuromuscular re-education, the prescribed exercises train the body to perform specific motions accurately through repetition. This improves the body’s muscle memory, reinforcing positive, ‘normal’ movement patterns.
Neuromuscular rehabilitation is useful for helping those who need to repair the biomechanics of their limbs and those who need to redevelop their full range of motion in areas where it has been lost due to injury or trauma, ultimately preventing future injuries into adulthood.

Sports injuries in children differ widely from those sustained by their adult counterparts. With an accurate diagnosis, a specific foot care and injury rehabilitation plan can be prescribed to ensure minimal time away from sports activities and full recovery.
Knowledge of the specific demands of individual and multi-sport activities, and of the biomechanics of children’s injuries, is where The Foot Practice’s clinical team excels. There are many reasons and benefits to kids playing sports, but as a parent, when they get injured, the ultimate goal is to create appropriate return-to-sport plans and rehabilitation programs to address any underlying risk factors for further or recurrent injury.
Schedule an appointment with our leading pediatric sports injury podiatrists to ensure your child’s foot, ankle, or lower limb condition is addressed properly so that they can safely return to sport for lifelong enjoyment.