Patellar tendonitis, or jumper’s knee, is a common overuse injury of the tendon that connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia). The patellar tendon is a key component of the lower body’s function, as it is responsible for knee extension and powers movements such as running, jumping, and kicking. When subjected to repeated stress, often from high-impact activities such as basketball, volleyball, or long-distance running, the tendon can develop microtears that cause inflammation and pain just below the kneecap.
If left untreated, the condition can get worse and lead to chronic patellar tendon pain and reduced performance. Early diagnosis and targeted treatments are crucial for effectively healing patellar tendonitis and preventing recurrence.
Causes and Risk Factors for Patellar Tendonitis
The leading cause of patellar tendonitis is repetitive stress on the patellar tendon. Naturally, risk factors for patellar tendonitis include sports that involve frequent jumping, running, or quick direction changes, such as football and tennis. Distance runners also develop this condition due to the repetitive knee extension during the push-off phase of their gait cycle. Muscle imbalances, poor training techniques, and inadequate warm-up and cool-down routines can also contribute to patellar tendonitis. Other risk factors include flat feet and weak leg muscles. A trained specialist can help you identify and address these risk factors to prevent patellar tendonitis and overall knee health.

The Mechanics of Jumper’s Knee
If you are wondering how to heal patellar tendonitis, it is essential to understand the biomechanical factors that contribute to its development. The condition develops gradually. Initially, you may feel mild discomfort only after intense training sessions, but as the condition progresses, patellar tendon pain can interfere with daily activities and performance.
Several factors contribute to the development of chronic patellar tendonitis. Poor biomechanics, muscle imbalances between the quadriceps and hamstrings, weak or tight thigh muscles, inadequate flexibility in the hip flexors and quadriceps, and training errors all contribute to the issue. Additionally, improper footwear that lacks sufficient shock absorption or motion control can alter lower limb mechanics and increase stress on the patellar tendon.
The Role of A Podiatric Assessment
Modern podiatric assessment combines traditional clinical examination with advanced biomechanical analysis to identify the root causes of patellar tendonitis. This comprehensive approach often reveals subtle gait abnormalities or foot positioning issues that cause abnormal loading patterns at the knee.
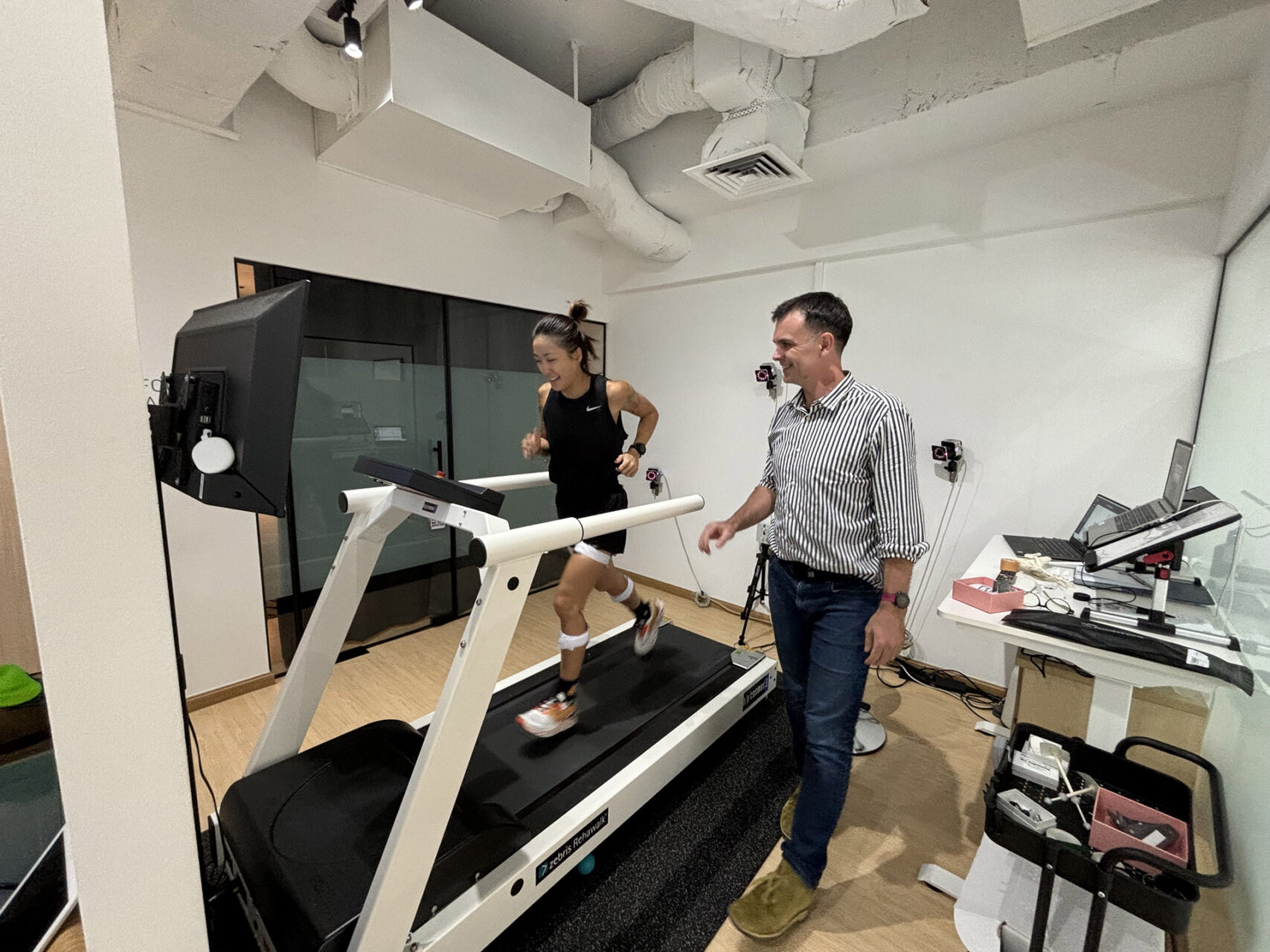
Advanced pressure sensor treadmill gait analysis, such as the RehaWalk® system, provides valuable insights into your movement patterns during walking and running. This technology captures real-time data about ground reaction forces, pressure distribution, and timing parameters that may not be apparent during static examination. These findings often reveal compensatory movement patterns that put excessive stress on the patellar tendon even when you’re not feeling symptoms.
The assessment process includes detailed footwear evaluation, as improper shoe selection can significantly affect lower limb biomechanics. Worn-out running shoes, inadequate arch support, or the incorrect shoe type for your foot structure and gait pattern can create a cascade of biomechanical compensations that manifest as knee pain. Importantly, there is no single way on how to cure patellar tendonitis. Holistic treatment options must be used in conjunction to achieve the best outcomes.

Can I Run with Patellar Tendinopathy?
The answer to this key question depends on the severity of your symptoms, your ability to modify activities, and your treatment options. Complete rest is rarely the best approach for patellar tendonitis, as controlled loading actually promotes tendon healing and remodelling.
Managing the condition effectively is key to preventing further injury. Modern treatment protocols focus on progressive loading strategies that allow the tendon to adapt gradually, avoiding over-stress and perpetuating the inflammatory cycle. This often means modifying training intensity and volume rather than altogether ceasing activity. Swimming, cycling and other low-impact activities can maintain cardiovascular fitness while the patellar tendon recovers.
Mobilisation exercises play a big role in addressing the muscle tightness and joint restrictions that often accompany patellar tendonitis. Targeted stretching of the quadriceps, hip flexors and calf muscles helps restore normal length-tension relationships and reduces stress on the patellar tendon. Specific mobilisation techniques for the patella itself can also improve tracking and reduce localised tension.

Non-Surgical Treatments
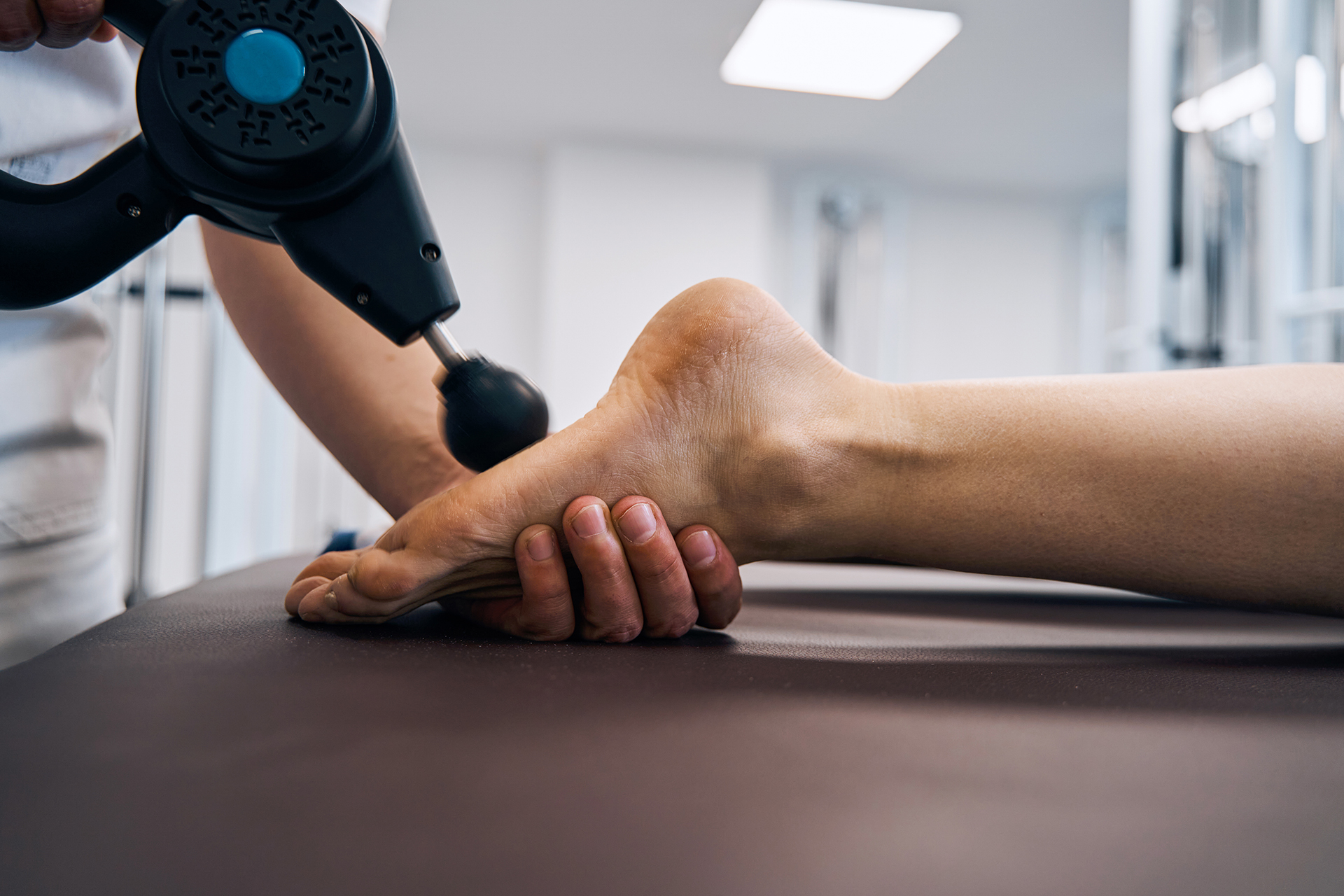
Non-surgical treatments for patellar tendonitis aim to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing and improve knee function. Common non-surgical treatments include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the leg muscles. Ultrasound and extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy may also promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, a corticosteroid injection may be administered to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalised treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes of patellar tendonitis.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for patellar tendonitis is typically reserved for cases that are severe and have not responded to non-surgical treatments. Surgery may involve removing damaged tissue, repairing the tendon, or reattaching the tendon to the kneecap. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that uses small incisions and a camera to visualise the joint and repair the tendon. Open surgery involves making a larger incision to access the tendon and fix it. Discussing the benefits and risks of surgical treatment with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best course of action.
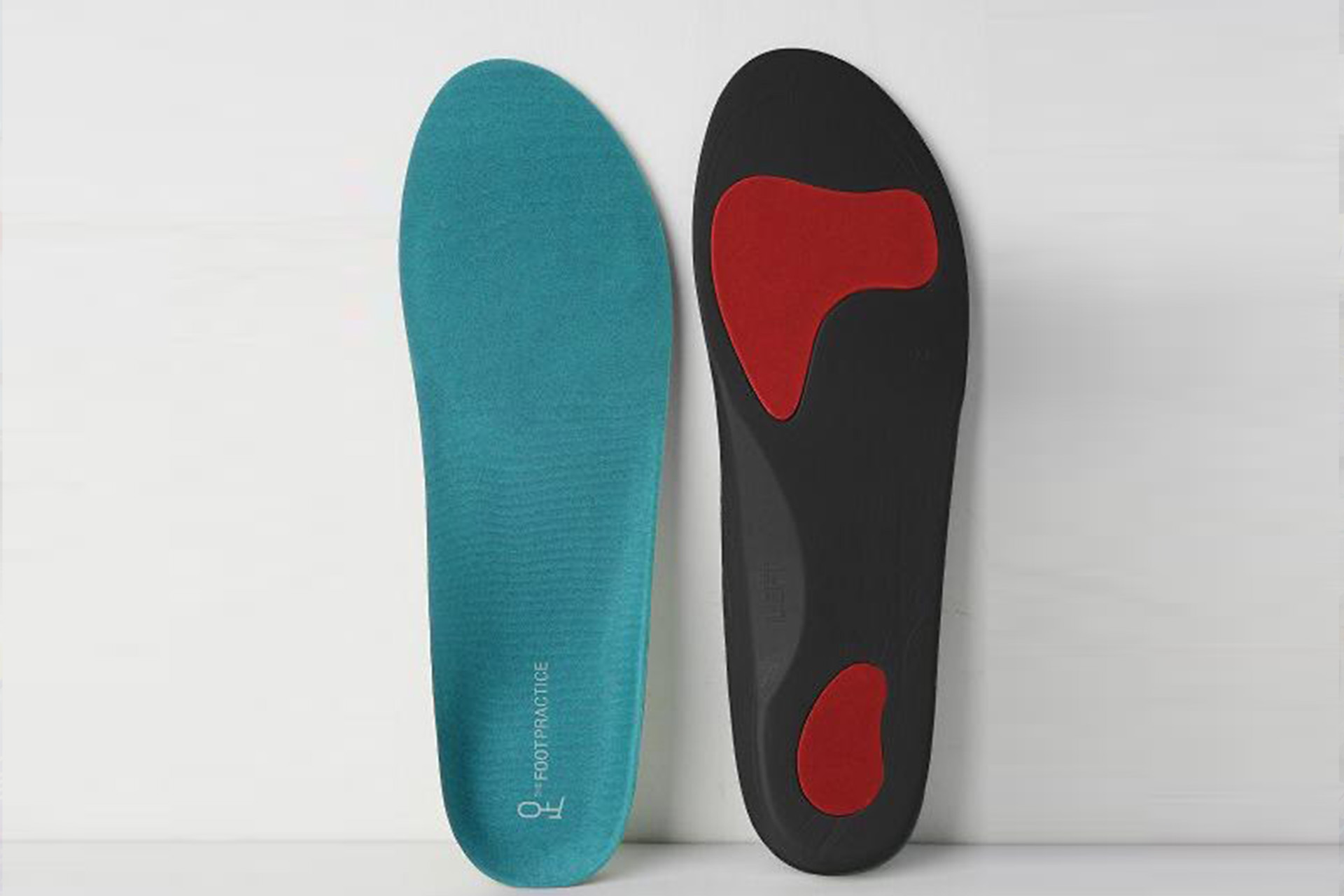
Custom Orthoses for Patellar Tendonitis
Custom orthoses are another cornerstone of comprehensive patellar tendonitis management. These precision-crafted insoles address underlying biomechanical dysfunction by optimising foot positioning and controlling excessive pronation or supination, which contributes to abnormal knee mechanics. The custom orthoses redistribute forces throughout the lower extremity, reducing the repetitive stress that perpetuates tendon inflammation.
Combining these modalities creates a synergistic effect that addresses the symptoms and underlying causes of your condition. Rather than relying on a single intervention, this comprehensive approach recognises that effectively curing patellar tendonitis requires addressing multiple contributing factors simultaneously.

Prevention and Long-Term Management
Overcoming patellar tendonitis requires more than symptom resolution. It requires addressing the underlying factors that contribute to the condition’s development. If you are too concerned with how to heal patellar tendonitis fast, you risk getting a recurring injury and compromising your long-term knee health.
Patellar tendonitis can be managed through regular biomechanical assessments, which identify subtle changes in movement patterns before they become symptomatic. Similarly, periodic footwear evaluations ensure that your shoes continue to provide support as they wear and as your biomechanical needs change with training adaptations.
Maintaining flexibility in key muscle groups, especially the quadriceps and hip flexors, helps preserve normal movement patterns and reduces stress on the patellar tendon. Incorporating variety into your training routine prevents repetitive stress patterns that often lead to overuse injuries.

Make An Appointment at The Foot Practice
If persistent knee pain is affecting your training or daily activities, a professional assessment and treatment can provide the clarity and direction you need to return to full activity. The Foot Practice’s combination of modern diagnostic tools, research-based treatment, and individualised care plan is the best way to treat patellar tendonitis and prevent it from returning.
Don’t let jumper’s knee keep you sidelined. Book an appointment with The Foot Practice today to get assessed and discover how our approach to patellar tendonitis treatment can help you get back to what you love, stronger and better than before.