Despite being a common condition, hypermobility often goes under the radar. Many people experience foot or body aches without knowing that hypermobility is the culprit. In Singapore, hypermobility is especially common and linked to flat feet, yet it is underdiagnosed. Thankfully, there are intervention strategies available for managing joint hypermobility syndrome pain.
What is Hypermobility?
Hypermobility is when joints move beyond their normal range of motion. It can affect the feet and lower limbs.
Joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a condition characterised by excessive joint laxity, leading to joint pain, instability and other symptoms, like muscle fatigue, which can significantly impact daily life. This disorder affects the body’s connective tissue, which provides support and structure to various organs, joints, and other tissues. Understanding the nature of hypermobility as a disorder is crucial for our podiatrist to help you manage its symptoms and improve your quality of life.

Types of Hypermobility
There are several types of hypermobility, including localised, generalised, benign joint syndrome and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (HSD), each with its own characteristics and demanding specific interventions:
- Localised Hypermobility: This affects specific joints like the ankle or knee and allows excessive movement beyond the normal range. In the feet, it can cause chronic instability, frequent sprains, collapse of the arches and exacerbate conditions such as flat feet.
- Generalised Hypermobility: This involves multiple joints across the body and is often associated with musculoskeletal symptoms like arthritis, muscle pain and instability. Severe cases may be linked to underlying conditions like Marfan Syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, which can weaken the structural integrity of the foot and ankle.
- Benign Hypermobility Syndrome: This milder form of hypermobility typically does not cause significant symptoms or problems. Individuals with this type of hypermobility may have increased hypermobility flexibility without severe pain or instability, especially if the condition does not affect their lower limbs, which bear more pressure.
- Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (HSD): This condition includes a range of symptoms beyond joint hypermobility, such as fatigue, headaches, and gastrointestinal problems. HSD represents a broader spectrum of issues that can accompany hypermobility.
Hypermobility causes include genetic factors like a defect in the Tenascin-X gene. It is more common in women and runs in families. Understanding these different types helps identify the specific challenges and appropriate management strategies for each form of hypermobility.

Hypermobility Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hypermobility symptoms like joint pain, weak or ineffective muscles, or poor coordination can manifest in many ways that affect daily life. It’s not uncommon to find a connection between hypermobility and back pain. Other common issues are gait abnormalities, frequent ankle sprains or injuries, and clicking or popping joints.
In children, hypermobility shows up as frequent tripping or falling. In adults, painful flat feet is often linked to joint hypermobility, where the arch collapses under weight-bearing and worsens the discomfort and instability.

When Do Hypermobility and Joint Pain Need Intervention?
Not everyone with hypermobility has symptoms or needs intervention. Many people, especially athletes, dancers or gymnasts, use their joint flexibility to their advantage. However, overextending joints can lead to injuries.
For some, hypermobility can be very uncomfortable or painful. If left untreated, it can lead to long-term complications such as:
- Chronic Pain Syndrome: Recurring pain due to joint instability and muscle overcompensation. Patients may be referred to a pain clinic, which provides specialised treatments and self-help skills to manage and alleviate pain if chronic pain from hypermobility does not improve with standard medical care.
- Malalignment Syndrome: Misalignment of the skeletal system that affects posture and gait.
- Osteoarthritis: Accelerated wear and tear on joints due to excessive range of motion and instability.
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD): Collapse of the foot arch due to overstretching and weakening of the posterior tibial tendon.
- Recurrent Sprains or Dislocations: Increased risk of soft tissue injuries from unstable joints.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine due to uneven joint loading and instability.
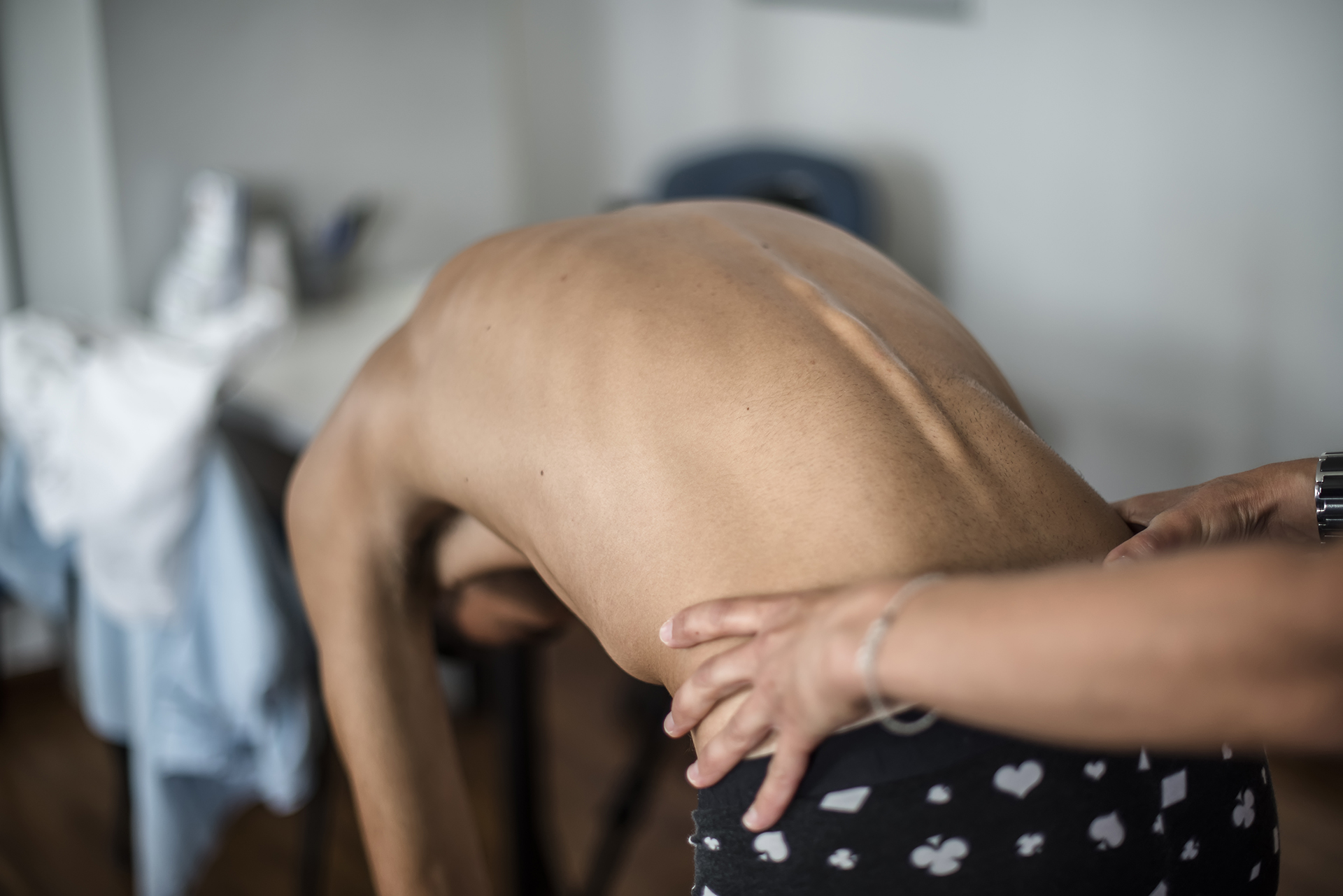
Why Stretching Isn’t Always the Answer
Stretching, which may seem like the obvious solution to muscle tension related to hypermobility, can actually worsen the problem. Tension occurs because muscles tighten to compensate for joint instability. Addressing the underlying hypermobility rather than increasing flexibility is the key to relief. This includes lifestyle modifications and professional care from a healthcare professional like a podiatrist.

How Podiatry and Physical Therapy help with Hypermobility
Podiatrists can play an impactful role in helping individuals with hypermobility to achieve joint stability and reduce pain. Here’s how podiatry can help:
- Exercise and Strengthening: Customised hypermobility exercise programmes can strengthen the muscles around hypermobile joints, allowing the muscles to provide better support. Improving muscle strength through hypermobility knee exercises, for example, is crucial for better joint support and reducing the risk of dislocations.
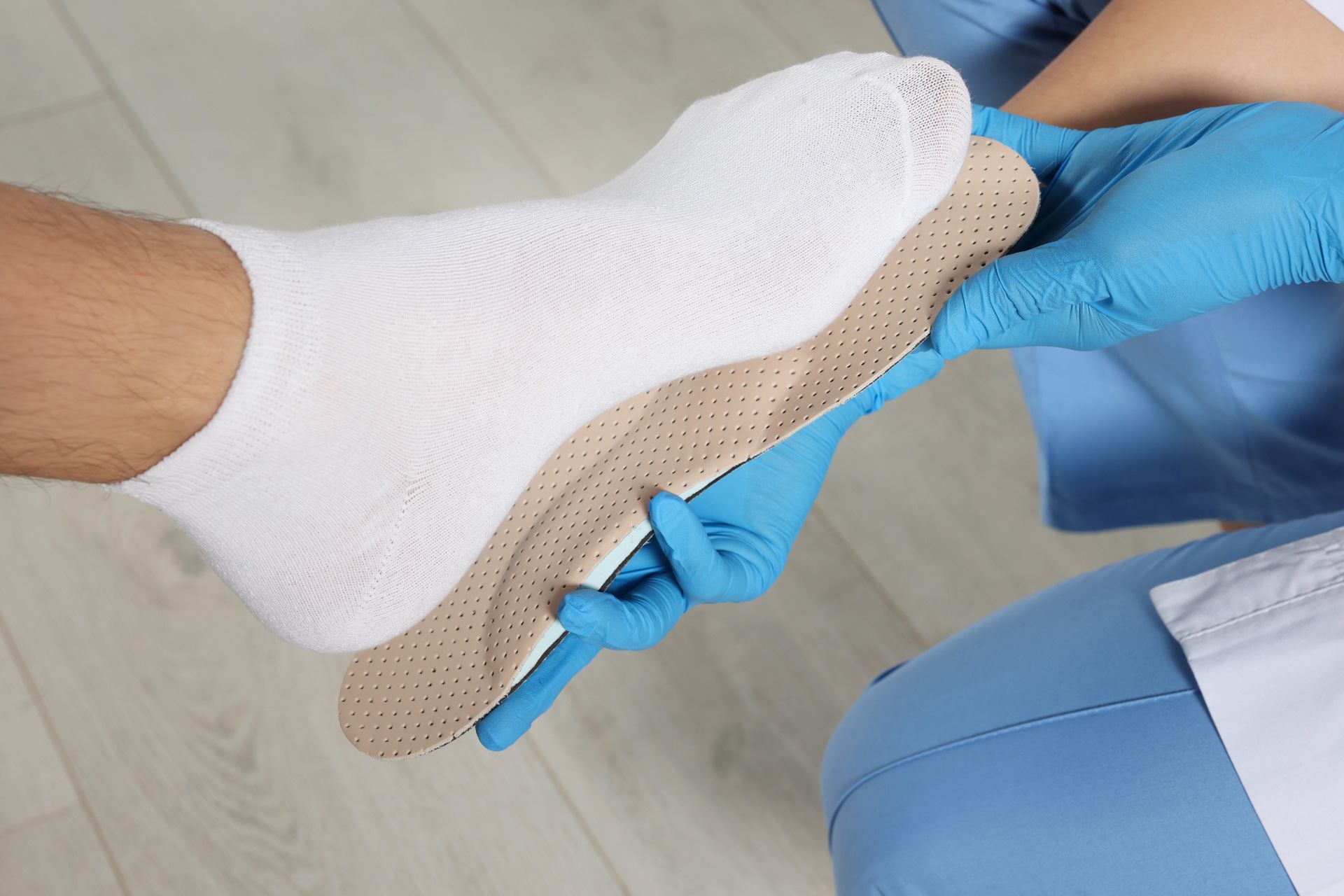
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotic devices such as ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) and knee braces stabilise joints and improve biomechanics, helping with hypermobility treatment. These devices can also address symptoms of flat feet related to hypermobility and reduce the risk of ankle sprains.
- Gait Analysis and Adjustments: Podiatrists use advanced tools like 3D gait analysis and RehaWalk® pressure sensor treadmill to identify abnormal movement patterns caused by hypermobility. This allows for interventions that promote proper alignment and efficient movement.
- Preventing Complications: Early intervention can prevent hypermobility-related complications such as tendinopathies, arthritis and recurrent joint injuries through individualised care.

Surgical Options for Severe Cases of Joint Hypermobility
If non-surgical conservative management is insufficient to address the condition, hypermobility surgery options may be considered to stabilise hypermobile joints. These procedures aim to improve joint integrity and relieve chronic pain for long-term improvement in quality of life.

Get Started Today
If you think you have hypermobility, or are experiencing symptoms, contact The Foot Practice for an assessment and individualised care. Our experienced podiatrists can help you prevent complications, achieve joint stability and get you moving again without pain.